发新帖
作者最近主题:
- Quaternized Silk Nanofibrils for Electricity Generation from Moisture and Ion Rectification. ACS Nano, 2020, Weiqing Yang; Lili Lv; Xiankai Li; Xiao Han; Mingjie Li; Chaoxu Li, DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.0c04686
- Nacre-based carbon nanomeshes for a soft ionic actuator with large and rapid deformation. Journal of Materials Chemistry C. X. Han; M. Kong; M. Li;* X. Li; W. Yang; C. Li*DOI: 10.1039/c9tc06186j
- Polymerization of moldable self-healing hydrogel with liquid metal nanodroplets for flexible strain-sensing devices. Chemical Engineering Journal. J. Xu, Z. Wang, J. You, X. Li, M. Li, X. Wu, C. Li* DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123788
- The synthesis of high-aspect-ratio Au microwires with a biomolecule for electrochemical sensing. Chemical Communication L. Lv, X. Han, X. Wu,* and Chaoxu Li*. DOI: 10.1039/c9cc06523g
- Peeling and Mesoscale Dissociation of Silk Fibers for Hybridization of Electrothermic Fibrous Composites. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering L. Lv, X. Han, X. Wu,* and Chaoxu Li* DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b05261
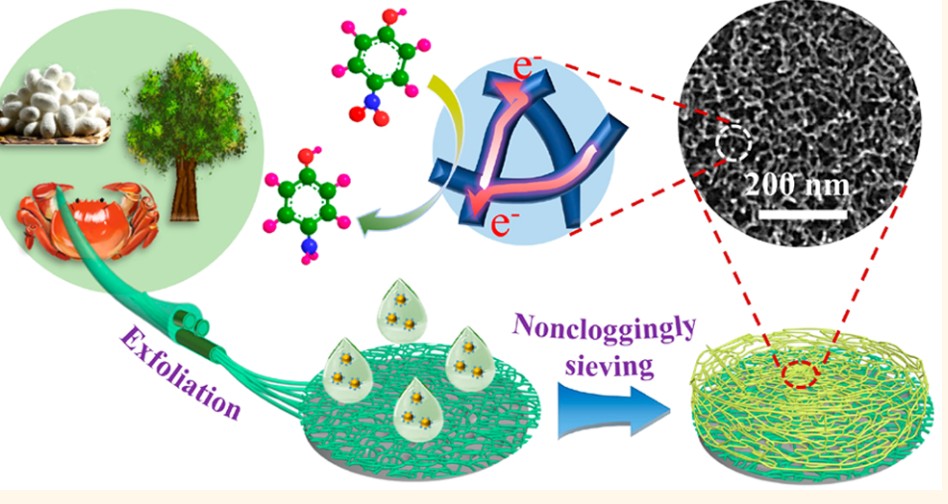
- Noncloggingly Sieving Sub‑6 nm Nanoparticles of Noble Metals into Conductive Mesoporous Foams with Biological Nanofibrils. ACS Nano Z. Wang, J. Xu, P. Wang, Y. Zhang, J. You,* and C. Li*. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.9b07923
- 一种液态金属/高分子复合介电材料的制备方法.李朝旭,徐洁,尤俊。申请号:201910261174.6。已申报,未授权。
- 李朝旭,李明杰,李现凯. 一种利用溶剂蒸发诱导液态金属微纳液滴融合烧结的方法: 中国, 201910334861.6.已申报,未授权。
- 李朝旭,李明杰,李现凯. 一种微米或纳米级液态金属水基分散液及其制备方法: 中国, 201810685133.5.已申报,未授权。
- 李朝旭,李明杰,韩笑. 一种基于珍珠层的碳纳米筛及其制备方法: 中国, 201811228796.0. 已申报,未授权。